All About Zeon
After 75 Years,
Zeon Remains Strong
as it Evolves with the Times
Founded in 1950, Zeon marked its 75th anniversary in 2025. Here we introduce the Company's business history and corporate culture underlying its innovative technological capabilities.
Business and Product Development History
Since its foundation, Zeon has steadfastly pursued and applied its innovative, proprietary technologies to product development. It has operated under the philosophy of "identifying customer and societal needs that are changing with the time and leading in the creation of products that address those needs." What follows is a brief review of our corporate history.
- 1950s
- 1960s
- 1970s
- 1980s
- 1990s
- 2000s
- 2010s
- 2020s
Following the period of manufacturing PVC and then synthetic rubbers, achieved remarkable growth in the C4 and C5 business.
In 1950, just after the end of World War II, Zeon Corporation was founded as a manufacturer of PVC. A technology for manufacturing PVC was introduced from U.S.-based B.F. Goodrich Chemical Company, then a world leader of the industry. In 1959, Zeon started manufacturing synthetic rubbers for the first time in Japan under the technical guidance of the Company. At the time, synthetic rubbers were only manufactured under a public-private partnership established under the Act on Special Measures Concerning Synthetic Rubber Manufacturing Business. Zeon was the first private company to manufacture synthetic rubbers. The supply of natural rubbers completely depended on imports from producer countries in Southeast Asia and other regions. However, the prices of natural rubbers then fluctuated sharply, largely conditional on the weather and political conditions of the exporting countries. The domestic manufacturing of synthetic rubbers was therefore urgently needed for the automotive and other manufacturing industries in Japan.
After achieving the domestic manufacturing of specialty rubbers (NBR, acrylonitrile butadiene rubber), Zeon Corporation started manufacturing general-purpose specialty rubber (SBR, styrene-butadiene rubber). The Company has developed its specialty rubber business with a focus on its application for tires and peripheral automotive engine parts.
Once we established a solid manufacturing system for synthetic rubbers using butadiene extracted from C4 fractions of crude oil as a raw material, we took on the development of isoprene rubbers. Since isoprene rubbers with properties equivalent to natural rubbers are highly useful, developing a technology to extract isoprene stably from C5 fractions became an urgent undertaking. As a result of our research, we identified a catalyst for efficiently extracting isoprene. What was more, we succeeded in producing additional byproducts.
In the 1980s, Zeon expanded its business to include petroleum resins and thermoplastic elastomer SIS, which use piperylene, dicyclopentadiene, and 2-butyne extracted from C5 fractions as raw materials. In the 1990s it added synthetic aroma chemicals and RIM molded products to its line-up, and then cyclo-olefin polymers in the 2000s. These businesses now enjoy a major share of the global market.
In recent years, the business of cyclo-olefin polymers, used for optical films, optical lenses, and medical devices, has been growing dramatically. It could be said that the technological capabilities for developing the series of raw materials required in each era has supported the 75 years of Zeon Corporation's history.
ZΣ Activities: A Company-wide Improvement Initiative
Aiming to strengthen its cost competitiveness while building a solid corporate structure, Zeon is conducting "ZΣ Activities" under its ongoing, Company-wide improvement campaign. The "Z" in "ZΣ" signifies the Zeon method, while "Σ" stands for combination, concentration of resources, and Company-wide participation. Zeon Corporation promotes management reform by placing ZΣ Activities at the core of its management system.

- Business model patent:
- patent No. 4134594
- Name of invention:
- "Theme management system and related program"
- Registration date:
- June 13, 2008
Four pillars of ZΣ
1 Clarify results of cost reductions by applying a small unit-based management system.
In ZΣ, we manage activities by small units called "Organs*" as required and promote activities. For each Organ, we specifically recognize the impact an Organ's operations have on Zeon's management and visualize the Organ's achievements.
- *A human body is organized to maintain its functions through organs acting in an organic manner. In the same way, an organization (such as a company) operates through the organization and functioning of "organs" (small units). Zeon therefore refers to its small units as "Organs."
2 Cost Management by Setting Account Titles
The figures that affect corporate management include: "A Values" related to the income statement, "CF" related to the statement of cash flows, and "V Values" associated with potentials such as productivity. We convert all these figures into costs, and we also set account titles so costs incurred by the themes of ZΣ correspond to those of items posted on financial statements.
3 Company-wide Optimization under the "Supply Chain" Concept
We work not only to improve the operations of each business division (division-wide optimization) but also to optimize the entire process in the operational flow, viewing all of it as a supply chain. This radically improves our corporate soundness under the philosophy of "regarding the next process as our customer."
4 Logical Problem-Solving and the Full Application of Scientific Methods
To consistently make improvements that do not require organizational changes, by identifying the root causes of problems and taking the appropriate actions, we learn quality control-based problem-solving methods (QC techniques, QC stories, and statistical techniques) rather than excessively rely on our experiences, intuition, and courage. In addition, we scientifically manage business operations using acquired data to achieve improvements.
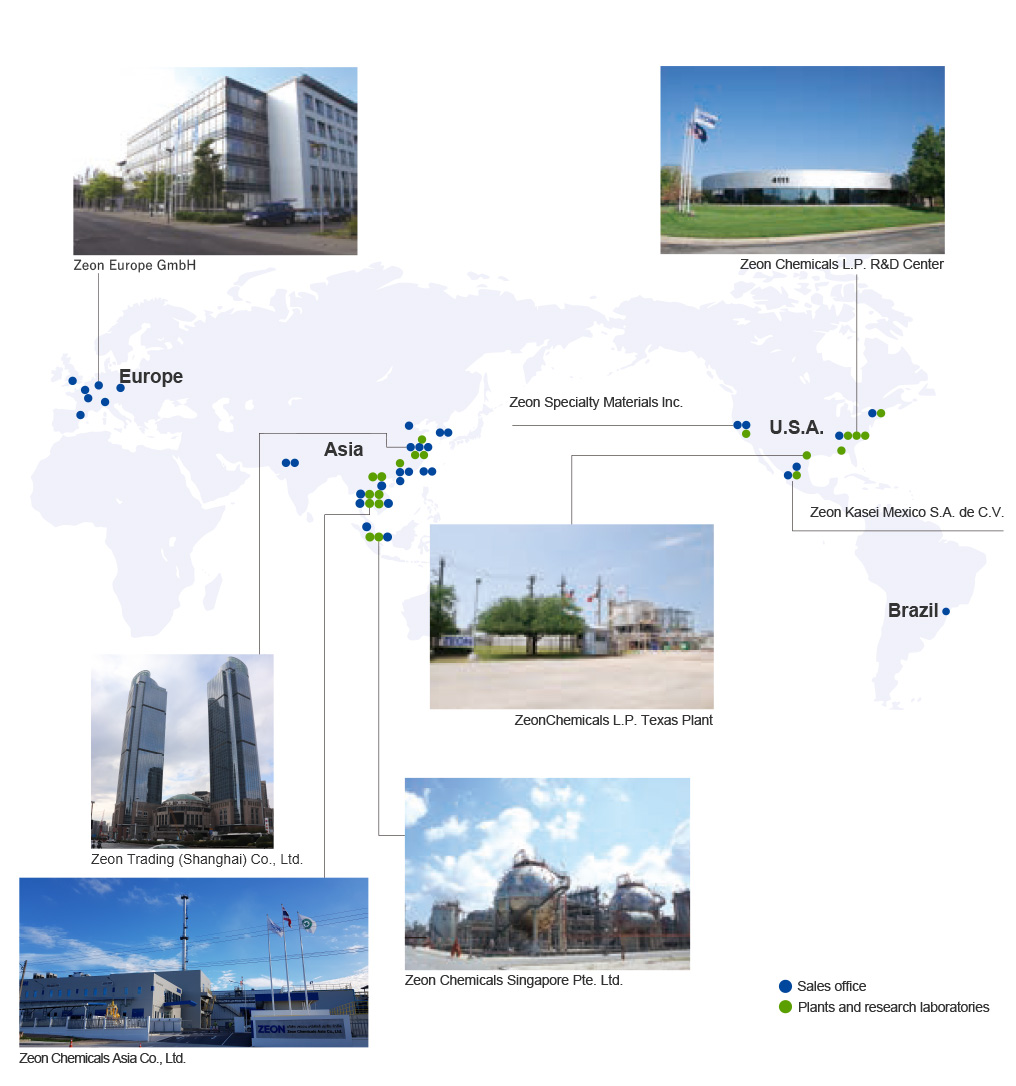
Globalization in Business
Since the 1970s, Zeon has been driving the globalization of its business from a global perspective. While establishing its sales network in major countries and regions, it has set up its manufacturing system, focusing on the Elastomer Business. We also operate technical support centers in the U.S., Europe, and Asia in order to respond quickly to local needs.