All About Zeon
Conducting a Broad Range of
Businesses Leveraging C5 Fractions
As a chemicals manufacturer, Zeon is engaged unique businesses using raw materials extracted from the C4 and C5 fractions in naphtha along with its proprietary technologies. The use of C5 fractions across a broad range of products is a particularly significant strength of Zeon and one source of its competitive strength.
About Zeon Corporation
Zeon Corporation was founded in 1950 with capital contribution from Furukawa Electric Co., Ltd., Yokohama Rubber Co., Ltd., and Nippon Light Metal Company, Ltd. It started business with the manufacturing of PVC, using PVC manufacturing technologies acquired from U.S.-based B.F. Goodrich Chemical Company. The Company subsequently developed its proprietary technologies to extract butadiene, isoprene, and other raw materials for synthetic rubbers and plastics, which it currently handles while continuing to manufacture and sell diverse petrochemical products.
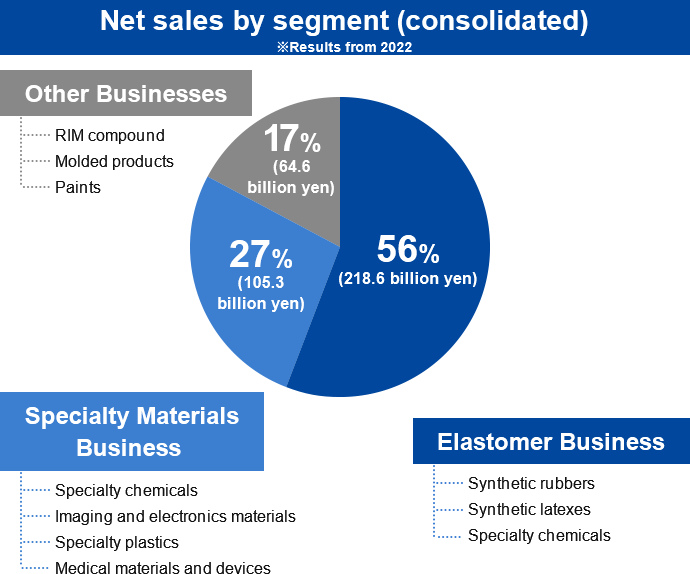
The Elastomer Business (Zeon's Core Business)
- Synthetic rubbers
- Synthetic latexes
- Chemical products (petroleum resins, thermoplastic elastomers)

Specialty Materials Business (Zeon's Recently Developing Venture)
- Specialty chemicals (synthetic aroma chemicals, other specialty chemicals)
- Imaging and electronics materials (polymerized toner)
- Specialty plastics (cyclo-olefin polymers)
- Specialty components (optical films)
- Energy materials (binders for lithium-ion batteries)
- Medical materials and devices

Other Businesses
RIM, paints, housing materials, etc.
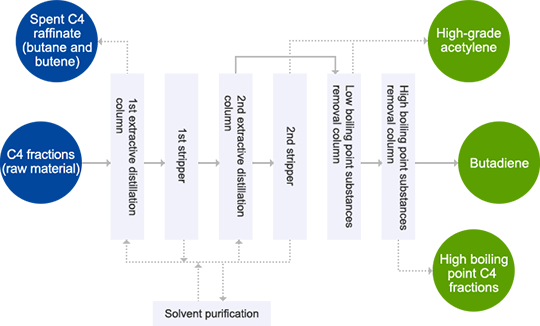
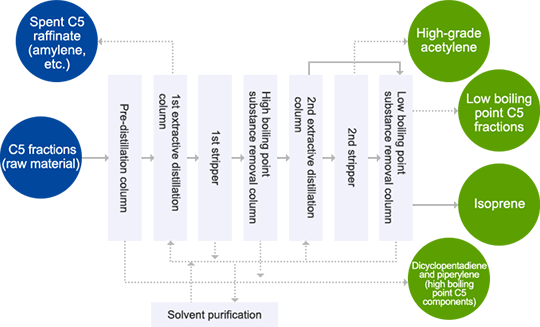
Zeon Corporation's Core Technology for Extracting C4 and C5 Fractions
The core business of Zeon Corporation consists of materials and products that include various components extracted from the C4 and C5 fractions in naphtha as raw materials, and it uses Zeon's proprietary technologies. We manufacture synthetic rubbers and synthetic latexes by extracting highly pure butadiene from C4 fractions using our proprietary GPB process. In addition to synthetic rubbers, we manufacture petroleum resin, cyclo-olefin polymers, and synthetic aroma chemicals by extracting isoprene, piperylene, dicyclopentadiene, and 2-butyne from C5 fractions while also using GPI technology.
The manufacture of synthetic rubbers has largely driven Zeon Corporation's growth. Initially, we only manufactured butadiene-derived synthetic rubbers that use C4 fractions as raw materials. Then, having expanded the synthetic rubbers business, we started the C5 business by manufacturing C5-derived isoprene rubber with the same chemical composition as natural rubber. However, while butadiene accounts for about 40% of C4 fractions, isoprene accounts for only about 10% of C5 fractions. If we were unable to effectively use components of C5 fractions other than isoprene, we would not be able to generate profits from the C5 business. We have therefore focused on research and development for effectively using C5 components. The GPI process to extract C5 components is also a proprietary technology, enabling us to develop diverse businesses under the umbrella of the comprehensive use of C5.
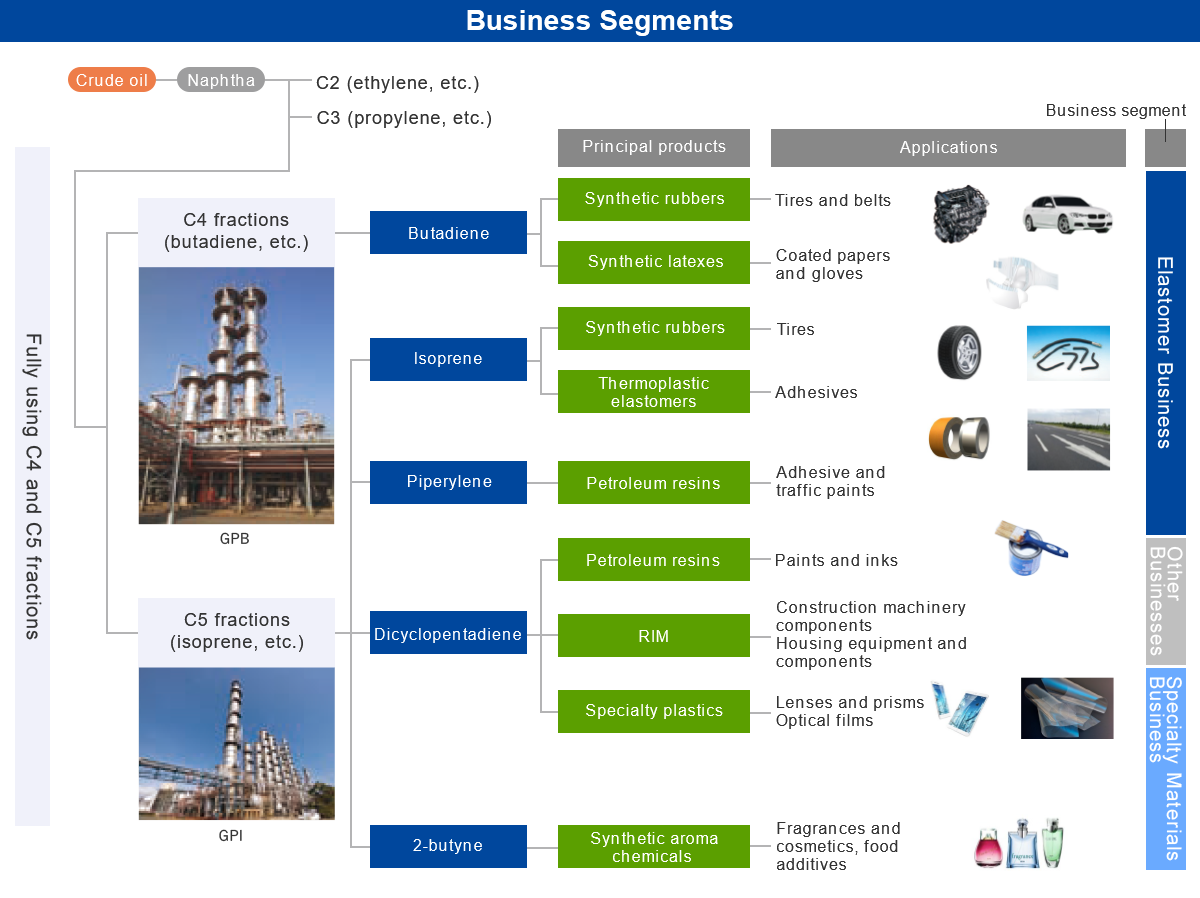
GPB process (butadiene extraction technology)
A technology for efficiently manufacturing highly pure butadiene (a major raw material for synthetic rubbers)
GPI process (isoprene extraction technology)
A technology for economically manufacturing highly pure isoprene, petroleum resins, synthetic aroma chemicals, and other useful components.
What are Fractions?
What do we mean by "fractions," as used in "C4 fractions" and "C5 fractions?" The word refers to components of a mixed liquid. For instance, crude oil fractions consist of naphtha, gasoline, jet fuel, kerosene, light oil, heavy oil, and so on. Each fraction can be extracted by distilling crude oil based on its boiling point. The boiling points for gasoline, kerosene, and light oil are 30-180°C, 170-250°C, and 240-350°C, respectively. Heavy oil and asphalt are the residues of crude oil after extracting these components.
The C4 and C5 fractions are finer and extracted by refining naphtha. The numbers "4" and "5" indicate the number of carbon atoms. C4 fractions have four carbon atoms and C5 fractions have five. The technological capability for extracting various raw materials from C4 and C5 fractions is Zeon's strength.
About Zeon's Business
Elastomer Business

The Elastomer Business is comprised of the three fields of synthetic rubbers, synthetic latexes, and chemical products, which constitute the foundation of Zeon. It provides high-quality materials essential for almost every industrial sector worldwide.
Since the Company started manufacturing synthetic rubbers for the first time in Japan in 1959, the synthetic rubbers business has been supporting Zeon as a solid business foundation, with a focus on special synthetic rubbers.
The synthetic latexes business provides various products widely used in everyday life, such as cosmetic puffs, paper coatings, and nonwoven fabrics. Chemical products are manufactured through the comprehensive use of C5 fractions and consist of petroleum resins that serve as the raw material for adhesives and thermoplastic elastomers. Zeon continues to focus on the development of new chemical products toward creating applications.
Specialty Materials Business

The Specialty Materials Business consists of specialty plastics, specialty chemicals, electronics materials, battery materials, and medical materials and devices.
Materials and products, such as specialty plastics used across a broad range of products, from camera lenses and medical devices to optical films used in TVs and smartphones, leverage their outstanding optical and other properties to deliver high added value through the application of macromolecular design and processing technologies. This business also encompasses a broad range of fields, such as specialty chemicals such as synthetic aroma chemicals and industrial chemicals, electronics materials for semiconductors, polymerized toner for printers, material for lithium-ion batteries, and medical devices.
Other Businesses
The main segments consist of the RIM business using dicyclopentadiene extracted from C5 fractions as the primary raw material, the paints business, and the building materials business. These ventures are largely conducted by Zeon Group companies.